
Shigeki Watanabe, Ph.D.
Department of Cell Biology
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
725 N. Wolfe Street, 100 Biophysics
Baltimore, MD 21205
Academic Titles
Associate ProfessorResearch Topic
High-resolution, ultrafast kinetics of synaptic membrane trafficking eventsResearch topic: Cellular and molecular characterizations of rapid changes during synaptic plasticity
For information processing and integration, neurons undergo rapid cellular and molecular reorganization. Presynaptically, synaptic vesicles undergo fusion with plasma membrane for neurotransmitter release. The vesicle membrane and proteins are recycled rapidly at synaptic terminals. Postsynaptically, the entire structure of the postsynaptic compartment, dendritic spines, can alter rapidly to mediate synaptic plasticity. At the molecular level, the addition of receptors to the surface of spines is associated with strengthening of synapses while their removal is associated with weakening and neurodegeneration. Many of these changes take place on a millisecond time scale. Despite the importance of these changes to the organism, remarkably little is known. Our goals are to characterize membrane and protein movements during synaptic transmission and plasticity. What is the composition and distribution of proteins in the synapse? What is the composition and distribution of lipids in the synapse? How does the activity alter the distribution of proteins and lipids? Ultimately, how does the misregulation of protein and lipid compositions lead to synaptic dysfunction? We aim to answer these questions using cutting-edge electron microscopy techniques in combination with molecular and biochemical approaches.
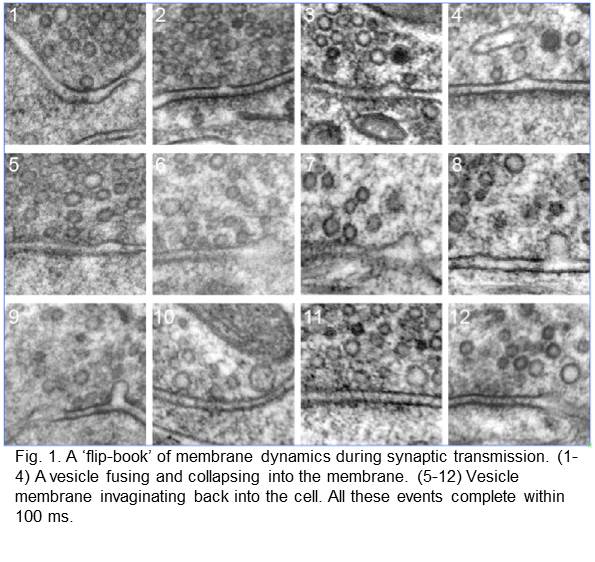
Membrane dynamics. We pioneered the “flash-and-freeze” approach that adds temporal information to electron micrographs. Electron microscopy traditionally only captures a static image of cells. To visualize membrane dynamics, we combined optogenetic stimulation of neurons with high-pressure freezing. By varying the intervals between stimulation and freezing, we can essentially make a “flip-book” of cellular dynamics at a millisecond temporal resolution.
Molecular topology and dynamics. We developed a correlative super-resolution fluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy approach that visualizes proteins in electron micrographs. We found a method that preserves fluorescence through harsh fixation and plastic embedding. We perform super-resolution and electron microscopy imaging on the same ultrathin sections of tissues and map the molecular topology onto the subcellular structures. This technique can be used to pinpoint the locations of proteins within their subcellular context.
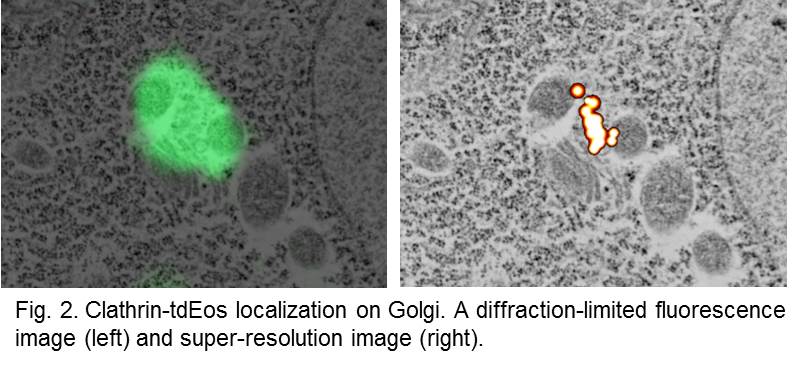
Using these approaches, we have discovered a novel endocytic pathway, ultrafast endocytosis, that removes vesicle membrane from plasma membrane within 100 ms after vesicle fusion. We have also demonstrated that clathrin regenerates synaptic vesicles from endosomes, not from plasma membrane, following a single action potential in mouse hippocampal neurons. Currently, we are studying the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying each step of vesicle recycling. In addition, we are studying the glutamate receptor trafficking at synapses.

